Prebiotics vs Probiotics-Difference, can they be taken together?
Prebiotics vs probiotics is quite an interesting subject when it comes gut know-how. What is the difference between prebiotics and probiotics in terms of definition, formulation how they are taken and health benefits? How are they similar? Can you take prebiotics and probiotics together?
Prebiotics vs Probiotics-What are they?
The human gut is a host of other microorganisms that have a critical role , not only in the breakdown of the foods that we ingest but also in the absorption of nutrients, the balancing of hormones in the body, strengthening of intestinal walls among others. As a host, it provides an operating environment for the microorganisms that live within them. These microorganisms are living organisms that are bound by the biological factors that relate to any living organisms.
For instance, all living organisms have a need to feed since their life requires energy to proceed on. Secondly, they have a need to reproduce – implying that they need to be fit to reproduce and increase in number while at the same time balancing their livelihoods with the available resources. Thirdly, they die. Microorganisms too experience the same, albeit in varying forms. The bacteria is one form that lives in the human gut. To meet these biological needs, they rely on prebiotics for nourishments.
What are Probiotics?
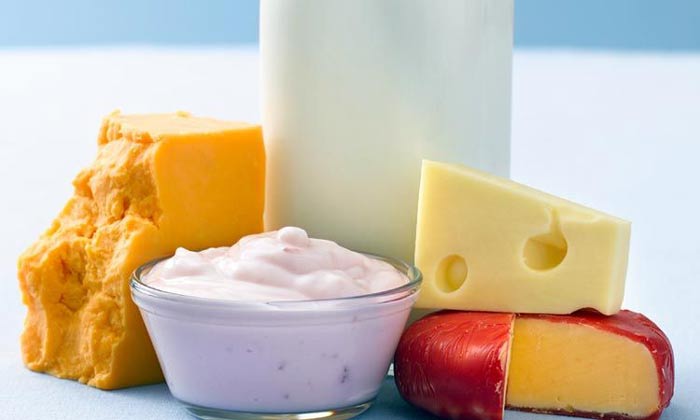
Probiotics are the microorganisms, specifically bacteria that inhabit or colonize the gut and serve to be of benefit to the host’s body. Particularly, the probiotics aid in the absorption of food in the gut, the strengthening of intestinal walls and have other functions they serve such as aiding in hormonal balancing.
Due to the positive effects that probiotics have in the human body, they are considered to be the good or beneficial bacteria. They have various other roles that they play such as aiding the body’s immune system by preventing or fending off the body from the harmful bacteria. These probiotics are available naturally from foods rich in them or from supplements.
Foods that are credited to have high numbers of probiotics include natural yoghurt, which is cultured naturally and has active ingredients. Other sources include;
- cheese
- sauerkraut
- miso
- tempeh
- sourdough bread
- kimchi among others.
Recommended reading
In situations where probiotic rich foods are unavailable, the use of supplements could aid. These products are available for kids, men and women. The supplements have been manufactured and each manufacturer avails them in varying forms such as capsules, tablets, chewable etc. settle for one that meets the current need. Where one is not very sure of the route to take, it is important to consult a medical practitioner to get further guidance.
What are prebiotics & food list
Prebiotics are those elements in the food that we take that are indigestible such that , once they are eaten, they proceed to the digestive tract without being digested but when they get to the colon, the good bacteria that lives there uses them to nourish themselves. These foods act as a source of nourishment for the probiotics that are present in the digestive tract.
The prebiotics can be introduced into the body by use of the natural foods that we take. A list is coming up shortly. However, getting the right amount from these foods is not easy. When one needs more fiber in their diet however, use of chicory root would be recommended. This root is considered rich in prebiotics and provides more feasible to ingest higher amounts of fiber.
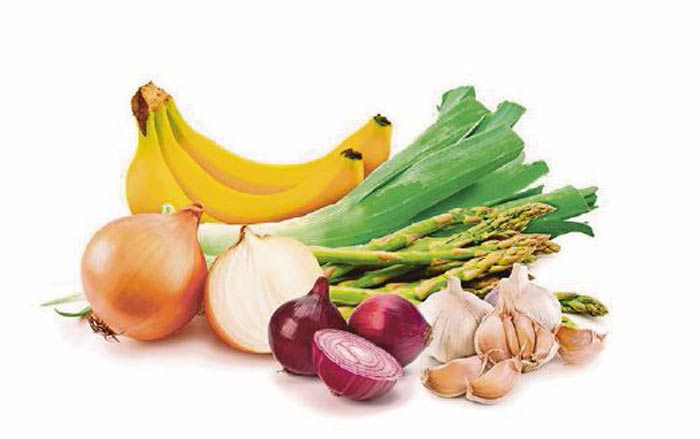
Here a list of more prebiotic natural foods
- asparagus
- carrots
- bananas
- garlic
- Jerusalem artichoke
- jicama
- apple
- leeks
- okra
- oatmeal
- onion
- radishes
- tomatoes
- turmeric
- cinnamon
- cereals
While the natural sources are many and varied, the use of supplements to meet the need for those who cannot get access to the natural food sources is a viable alternative. There are supplements that provide prebiotics only while others avail both prebiotics and probiotics.
Prebiotics vs Probiotics-What is the difference between prebiotics and probiotics?
Differences between Prebiotics and Probiotics
How do probiotics and prebiotics differ? What are the differences between the two? While both prebiotics and probiotics serve to aid the body, the mystery of their differences and or similarities to the majority seems to grow. Here, are some of the key similarities as well as some of the differences to aid in a better understanding.
Difference #1
The food sources from which either of them is derived vary to some extent. However, they are all found either in naturally occurring foods such as yoghurt for probiotics and bananas for prebiotics. Similarly, the are both also found in supplements whereby some may be found in tablets, capsules or even in powdered form. There are supplements that contain both probiotics and prebiotics such that should one ingest them; they get the value of having both.
Difference #2
Basing mainly on their role, their nature and reaction to varying elements they may encounter. For instance, by their definition, prebiotics are a special form of fiber found in the diet that you take. Probiotics on the other hand are live bacteria that are present either in the foods we take, the drinks or supplements that we consume. As such, while one is a food component or element, the other is a living microorganism.
Difference #3
In order to derive benefits from probiotics, they must be kept alive. Since they are living, when exposed to some conditions, just like other living organisms they may die. For instance, heat and stomach acid may lead to the death of these microorganisms. Prebiotics, when exposed to these same factors would not be affected since they are not affected by acid, time, heat or cold.
Difference #4
In comparison with other bacteria that is living in the human gut, probiotics are destined to compete with other bacteria strains for the resources and colonization environments with other bacteria that already live in the gut. However, the prebiotics are not exposed to this kind of competition since they nourish the good bacteria that the host already has.
Difference #5
In terms of the health benefits they provide, prebiotics offer a wide range of health benefits to the otherwise healthy person. Most of these have been medically proven. Probiotics on the other hand are still not clearly known to provide health benefits to the otherwise healthy. Some are suspected but still not proven.
Similarities
Do prebiotics and probiotics have similarities?
In terms of their operational environment, both probiotics and prebiotics operate within the human body, more specifically in the digestive tract. While one is used to actively aid the body in various ways, the other supports it. I.e. probiotics aid the body’s gut improve while prebiotics aid the probiotics with sufficient nourishment to enable them undertake their roles.
Both are not digested by the body’s digestive system. Probiotics when ingested are not broken down into glucose form as other foods, such as carbohydrates are. Instead, they get close to the end of the digestive tract intact. Under favorable conditions, they proceed to colonize the gut and establish a nice intestinal flora.
Similarly, the prebiotics too are not digested by the body’s digestive system. Their nature is such that, when they get into the body, the body is unable to digest them thus the body is not able to break them down as it breaks down other foods that are ingested. As such, they proceed down the digestive tract into the colon where the earlier consumed probiotics are living. This is where the probiotics use them for nourishment.
Both probiotics and prebiotics have an impact in the digestive health of individuals, for instance, prebiotics have been noted to be beneficial for varying conditions such as chronic digestive disorders and inflammatory bowel diseases. Similarly, probiotics have advantages associated to their use in that they are shown to be helpful to children who have diarrhea for instance or those with recurrent bowel infections such as C. deficile.
Prebiotics vs probiotics which is better?
In increasing the bacterial count in the body, both prebiotics and probiotics have a distinct role to play as described above. In terms of consumption and ingestion of either from the natural elements that host them, the foods vary.
Despite this, for individuals attracted by the taste of the foods, it depends on their preference for one product against another. Presence of both prebiotics and probiotics in the body has relevance to the sustenance of the health of each individual, but as a consumer, the deriving of direct benefits from the foods that are rich in prebiotics does not happen.
In fact, prebiotic rich foods are not digestible by the normal digestive system and thus they serve to load the digestive system with items that are not digestible. While this is a setback in theory, it works to the larger good in that their indigestibility leads to them having nourishing content for the probiotics which in turn aid the body in absorbing foods, breaking down some, boosting the immune system among others. As such, a clear cut line on the goodness or appropriateness of one against another may not be directly recognized due to the complexity in the value they avail to the body, whether directly or indirectly.
Can you take Prebiotics and Probiotics together?
YEs! You can take probiotics and prebiotics together. It is safe. There are no known complications associated with taking the together. Prebiotics neither negatively interact with probiotics nor do they interfere with medications.
When you take probiotics you add to millions of friendly bacteria to your microbiome and when you take prebiotics , the friendly bacteria that’s already in your gut is nourished. Taking them together means supplementing and nourishing at the same time.
Prebiotics and Probiotics Supplements, Capsules & Products
Prebiotic and probiotic products/supplements are readily available in the market. If you like going natural, the some of the foods listed above should be enough for you.
For those who prefer supplements in form of pills, capsules, gummies etc, below is a list of the best and most popular products
Best Probiotics products
- Culturelle Reviews
- Align Reviews
- Florastor Reviews
- Garden of Life Probiotics
- HyperBiotics
- Bio-Kult
- PB8
- Dr.Ohhira
Best Prebiotic Supplements
- Hyperbiotics Organic Prebiotic Fibre
- Fibre choice
- Dr Tobias Ultimate Prebiotic
- Now Inulin Prebiotic
Prebiotics and Probiotics Weight Loss
There is some evidence that both probiotics and prebiotics can in weight loss. For a detailed discussion on how probiotics may help you lose weight check this article: Best probiotics for weight loss
On prebiotics for weight loss mbd recommends
- Cal-mag butyrate, 200 to 300 mg, one to two times a day. Butyrate is both a prebiotic and a weight loss supplement.
- Inulin powder: 4 to 6 grams a day, divided into two doses.
- Arabinogalactans, 500 to 1000 mg, two times a day